Japanese cherry blossom-derived lactic acid bacteria (Somei-Yoshino strain)
Japanese cherry blossom-derived lactic acid bacteria (Somei-Yoshino strain)
What Is Japanese cherry blossom-derived lactic acid bacteria?
“Japanese cherry blossom-derived lactic acid bacteria (Somei-Yoshino strain)” is our proprietary lactic acid bacterium strain, isolated from the flowers of ‘Somei-Yoshino’, a cherry blossom species that symbolizes Japan. It exhibits a range of beneficial functionalities suitable for modern applications, including the promotion of bifidobacteria growth, antibacterial activity, improvement of the skin’s resident bacterial balance, and GABA production.Background of Development
Our company has long focused on plant extracts in product development and joint research. In doing so, we turned our attention to Japan’s iconic flower—the cherry blossom (Somei-Yoshino), which carries the symbolic meanings of “purity” and “exceptional beauty. ” True to this symbolism, we discovered a lactic acid bacterium with wide-ranging functional capabilities. It retains activities such as promotion of bifidobacteria growth, antibacterial effect, balancing skin resident bacteria, and GABA production. Additionally, we have newly identified a strain that induces the expression of longevity-related genes (sirtuin genes), paving the way for applications in health foods, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.About Functional Lactic Acid Bacteria
Fermented Foods and Lactic Acid Bacteria Long Celebrated in Japanese Culture

Fermented foods such as miso, soy sauce, and pickles have long been integral to human food culture, supporting dietary life. Recent research has revealed that the lactic acid bacteria in these fermented foods possess diverse physiological functions—particularly “tertiary functions” related to health. Functions such as intestinal regulation, immune enhancement, blood pressure reduction, and improved lipid metabolism are increasingly being recognized. Nowadays, lactic acid bacteria are not limited to yogurt—they are also incorporated into confectionery and beverages, boosting health-supportive features across various products.
Bifidobacteria Growth Promotion
Bifidobacteria help suppress the growth of harmful bacteria, maintain intestinal balance, and exert a variety of health benefits—such as weight management, prevention of constipation, enhanced immunity, allergy relief, improved skin condition, reduced cholesterol, diabetes prevention, and stress relief. The ability to promote bifidobacteria growth is thus highly valued.
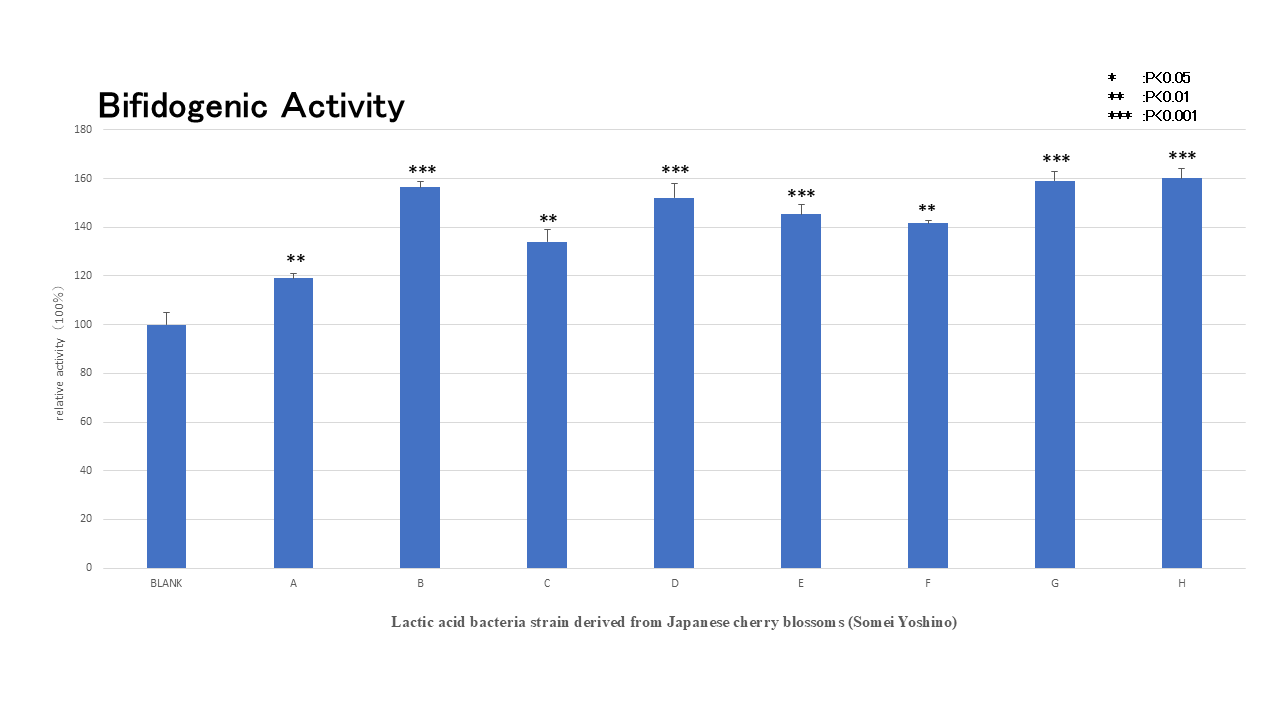
About Sirtuin Genes
What Are Sirtuin Genes?
Known as “longevity genes,” sirtuin genes play a crucial role in regulating aging and lifespan—central to achieving whole-body anti-aging effects.Role of Sirtuin Genes
When activated, sirtuin genes produce sirtuin (an enzyme/protein). Sirtuin is believed to suppress reactive oxygen species (which contribute to aging and cancer), activate immune antibodies that combat pathogens, and scan and repair cellular genetic material throughout the body—providing profound anti-aging effects.Types of Sirtuin Genes
There are seven varieties, SIRT1 through SIRT7, each with distinct functions. Among them, SIRT1 is the most extensively studied, showing anti-aging effects across various tissues.SIRT1 Effects
Improvement of wrinkles and spots, enhanced skin barrier function, increased ceramide synthesis, mitochondrial activation
SIRT2–7 Functions
・SIRT2 (cytoplasm): cell cycle, motility, myelin formation
・SIRT3 (mitochondria): fatty acid oxidation, antioxidant control
・SIRT4 (mitochondria): insulin secretion, inhibition of fatty acid oxidation
・SIRT5 (mitochondria): urea cycle
・SIRT6 (nucleus): genome stabilization, metabolism, lifespan extension
・SIRT7 (nucleolus): rDNA transcription
Sirtuin Gene Expression–Inducing Activity
Typically, sirtuin genes are activated through moderate exercise, calorie restriction, or intake of antioxidants. We aim to promote sirtuin gene activation through the application of lactic acid bacteria that exhibit this inducing activity.Additional Functionalities of Japanese cherry blossom-derived lactic acid bacteria (Somei-Yoshino strain)
Potential Applications in Food, Cosmetics, and Pharmaceuticals
Beyond its sirtuin gene–inducing activity, Japanese cherry blossom-derived lactic acid bacteria (Somei-Yoshino strain) offer a broad range of beneficial functions. Leveraging these functionalities, applications in everyday products—such as foods and cosmetics—as well as pharmaceuticals, are promising.GABA Production Activity
GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid naturally present in the human brain, known to reduce tension and stress, calm neural excitation, improve sleep quality, and help lower blood pressure. This bacterium’s ability to produce GABA is therefore highly beneficial.
Fibroblast Activation
Fibroblasts produce dermal components like collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid. By activating (i.e., promoting the growth of) fibroblasts, this bacterium may help suppress wrinkles and sagging—key signs of aging.
Improvement of Skin Resident Bacterial Balance
Skin resident bacteria include types such as Staphylococcus epidermidis, Cutibacterium acnes, and Staphylococcus aureus. Imbalance in these communities can lead to skin trouble. This bacterium helps stabilize the skin’s microbial balance and supports its barrier function.
Antibacterial Activity
Antibacterial activity refers to creating an environment unfavorable for bacteria proliferation through inhibitory effects.
